错误处理
错误可分为两类:预期错误和未捕获异常。本页将引导您了解如何在 Next.js 应用程序中处理这些错误。
处理预期错误
预期错误是指在应用程序正常运行期间可能发生的错误,例如服务器端表单验证或请求失败。这些错误应明确处理并返回给客户端。
服务器函数
您可以使用 useActionState 钩子来处理 服务器函数 中的预期错误。
对于这些错误,避免使用 try/catch 块并抛出错误。相反,将预期错误建模为返回值。
'use server'
export async function createPost(prevState: any, formData: FormData) {
const title = formData.get('title')
const content = formData.get('content')
const res = await fetch('https://api.vercel.app/posts', {
method: 'POST',
body: { title, content },
})
const json = await res.json()
if (!res.ok) {
return { message: 'Failed to create post' }
}
}您可以将操作传递给 useActionState 钩子,并使用返回的 state 来显示错误消息。
'use client'
import { useActionState } from 'react'
import { createPost } from '@/app/actions'
const initialState = {
message: '',
}
export function Form() {
const [state, formAction, pending] = useActionState(createPost, initialState)
return (
<form action={formAction}>
<label htmlFor="title">Title</label>
<input type="text" id="title" name="title" required />
<label htmlFor="content">Content</label>
<textarea id="content" name="content" required />
{state?.message && <p aria-live="polite">{state.message}</p>}
<button disabled={pending}>Create Post</button>
</form>
)
}服务器组件
在服务器组件中获取数据时,您可以使用响应有条件地渲染错误消息或redirect。
export default async function Page() {
const res = await fetch(`https://...`)
const data = await res.json()
if (!res.ok) {
return 'There was an error.'
}
return '...'
}未找到
您可以在路由段中调用 notFound 函数,并使用 not-found.js 文件显示 404 UI。
import { getPostBySlug } from '@/lib/posts'
export default async function Page({ params }: { params: { slug: string } }) {
const { slug } = await params
const post = getPostBySlug(slug)
if (!post) {
notFound()
}
return <div>{post.title}</div>
}export default function NotFound() {
return <div>404 - Page Not Found</div>
}处理未捕获的异常
未捕获异常是指意外错误,表明应用程序正常流程中不应发生的错误或问题。这些错误应通过抛出错误来处理,然后由错误边界捕获。
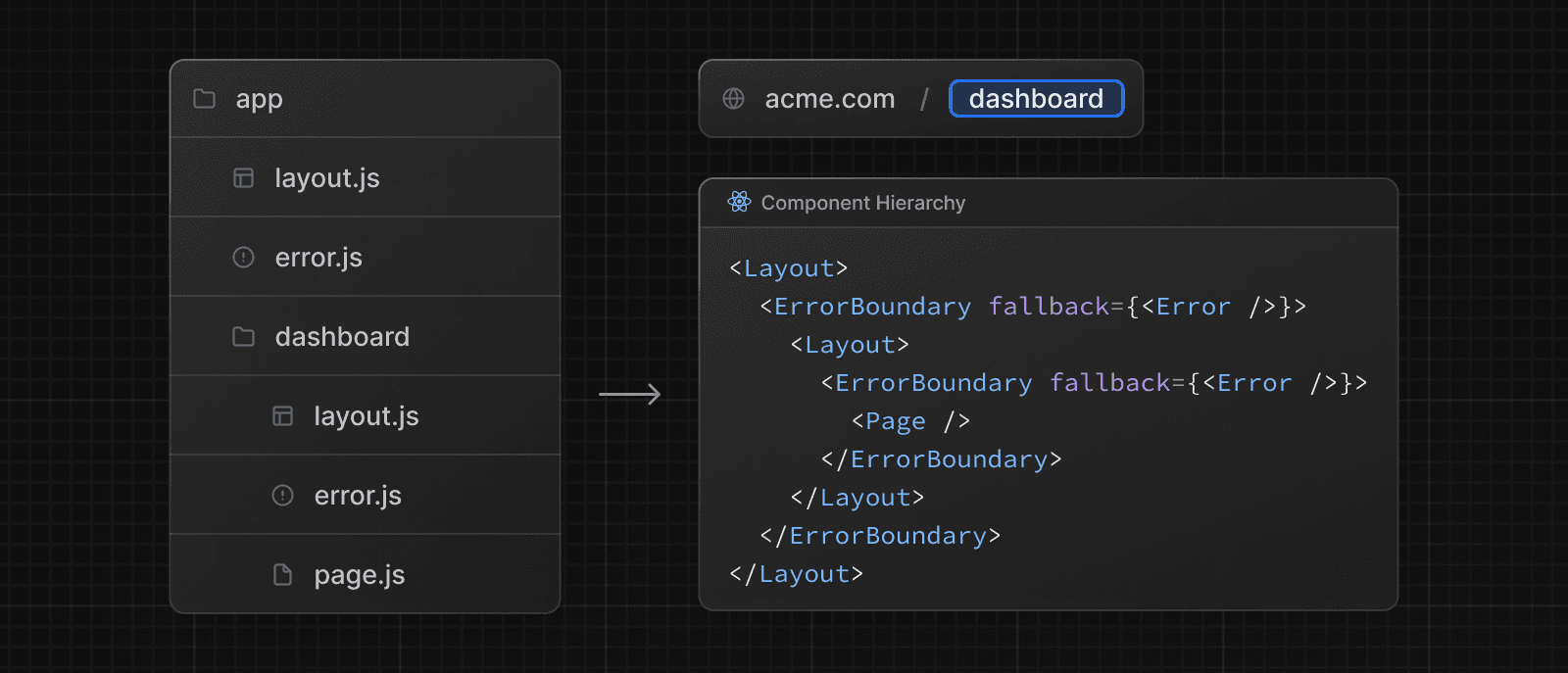
嵌套错误边界
Next.js 使用错误边界来处理未捕获异常。错误边界捕获其子组件中的错误,并显示备用 UI,而不是崩溃的组件树。
通过在路由段内添加一个 error.js 文件并导出 React 组件来创建错误边界
'use client' // Error boundaries must be Client Components
import { useEffect } from 'react'
export default function Error({
error,
reset,
}: {
error: Error & { digest?: string }
reset: () => void
}) {
useEffect(() => {
// Log the error to an error reporting service
console.error(error)
}, [error])
return (
<div>
<h2>Something went wrong!</h2>
<button
onClick={
// Attempt to recover by trying to re-render the segment
() => reset()
}
>
Try again
</button>
</div>
)
}错误将冒泡到最近的父错误边界。这允许通过在路由层次结构的不同级别放置 error.tsx 文件来实现细粒度的错误处理。
错误边界不捕获事件处理程序内的错误。它们旨在捕获渲染期间的错误,以显示备用 UI,而不是使整个应用程序崩溃。
通常,事件处理程序或异步代码中的错误不被错误边界处理,因为它们在渲染之后运行。
要处理这些情况,请手动捕获错误并使用 useState 或 useReducer 存储它,然后更新 UI 以通知用户。
'use client'
import { useState } from 'react'
export function Button() {
const [error, setError] = useState(null)
const handleClick = () => {
try {
// do some work that might fail
throw new Error('Exception')
} catch (reason) {
setError(reason)
}
}
if (error) {
/* render fallback UI */
}
return (
<button type="button" onClick={handleClick}>
Click me
</button>
)
}请注意,useTransition 中的 startTransition 内的未处理错误将冒泡到最近的错误边界。
'use client'
import { useTransition } from 'react'
export function Button() {
const [pending, startTransition] = useTransition()
const handleClick = () =>
startTransition(() => {
throw new Error('Exception')
})
return (
<button type="button" onClick={handleClick}>
Click me
</button>
)
}全局错误
虽然不常见,但您可以使用位于根 app 目录中的 global-error.js 文件来处理根布局中的错误,即使在使用国际化时也是如此。全局错误 UI 必须定义自己的 <html> 和 <body> 标签,因为它在激活时会替换根布局或模板。
'use client' // Error boundaries must be Client Components
export default function GlobalError({
error,
reset,
}: {
error: Error & { digest?: string }
reset: () => void
}) {
return (
// global-error must include html and body tags
<html>
<body>
<h2>Something went wrong!</h2>
<button onClick={() => reset()}>Try again</button>
</body>
</html>
)
}API 参考
这有帮助吗?